Creating a Personal Budget
Managing your finances effectively starts with understanding where your money goes each month. A well-crafted budget not only helps you take control of your finances but also enables you to save for your future goals. Finding a budgeting method that suits your lifestyle is key. Here are six essential steps to guide you in creating a budget that works for you.
Step 1: Calculate Your Net Income
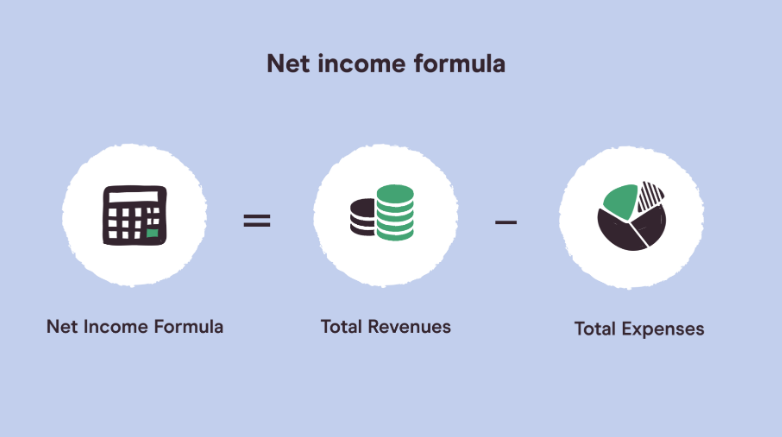
At the core of any effective budget lies your net income, which is your take-home pay after deductions like taxes, retirement contributions, and health insurance premiums. It’s crucial to focus on net income rather than gross earnings to avoid overspending. Freelancers, gig workers, contractors, and self-employed individuals should meticulously track their income to manage fluctuating earnings effectively.
Step 2: Track Your Spending
Once you have a clear picture of your income, the next step is to monitor your expenses. Start by listing your fixed expenses such as rent, utilities, and car payments. Then, identify variable expenses like groceries, gas, and entertainment, which may fluctuate monthly. Analyzing your credit card and bank statements can provide insights into where your money is going. Utilize tools such as budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even pen and paper to record your daily expenditures.
Step 3: Set Realistic Goals
Before diving into the details of your spending habits, establish both short-term and long-term financial goals. Short-term goals could include building an emergency fund or paying off credit card debt within the next one to three years. Long-term goals might involve saving for retirement or funding your child’s education over several decades. While goals can evolve, having them in place helps maintain focus and motivation, making it easier to adhere to your budget.
Step 4: Make a Plan
Now, consolidate the information gathered into a comprehensive plan. Compare your projected expenses with your net income and prioritize your financial goals accordingly. Establish realistic spending limits for each expense category, distinguishing between necessities and discretionary spending. For instance, commuting costs are essential, while optional subscriptions fall under discretionary spending. This differentiation helps in reallocating funds toward achieving your financial objectives.
Step 5: Adjust Your Spending to Stay on Budget
With your budget outlined, adjust your spending habits as necessary to avoid exceeding your financial limits and to allocate funds towards your goals effectively. Start by evaluating discretionary spending areas. For example, opting for a movie night at home instead of at the theater can save money. If further adjustments are needed, consider reviewing fixed expenses like insurance policies to find potential savings. Small changes in spending habits can accumulate significant savings over time.
Step 6: Review Your Budget Regularly

Once your budget is established, regularly review it along with your spending patterns. Circumstances change—whether through salary adjustments, shifting expenses, or achieving financial milestones—requiring periodic updates to your budget. Regularly revisiting these steps ensures your budget remains relevant and effective in guiding your financial decisions.
By following these steps, you can create a personalized budget that empowers you to manage your finances proactively, achieve your financial goals, and secure your financial future effectively.



